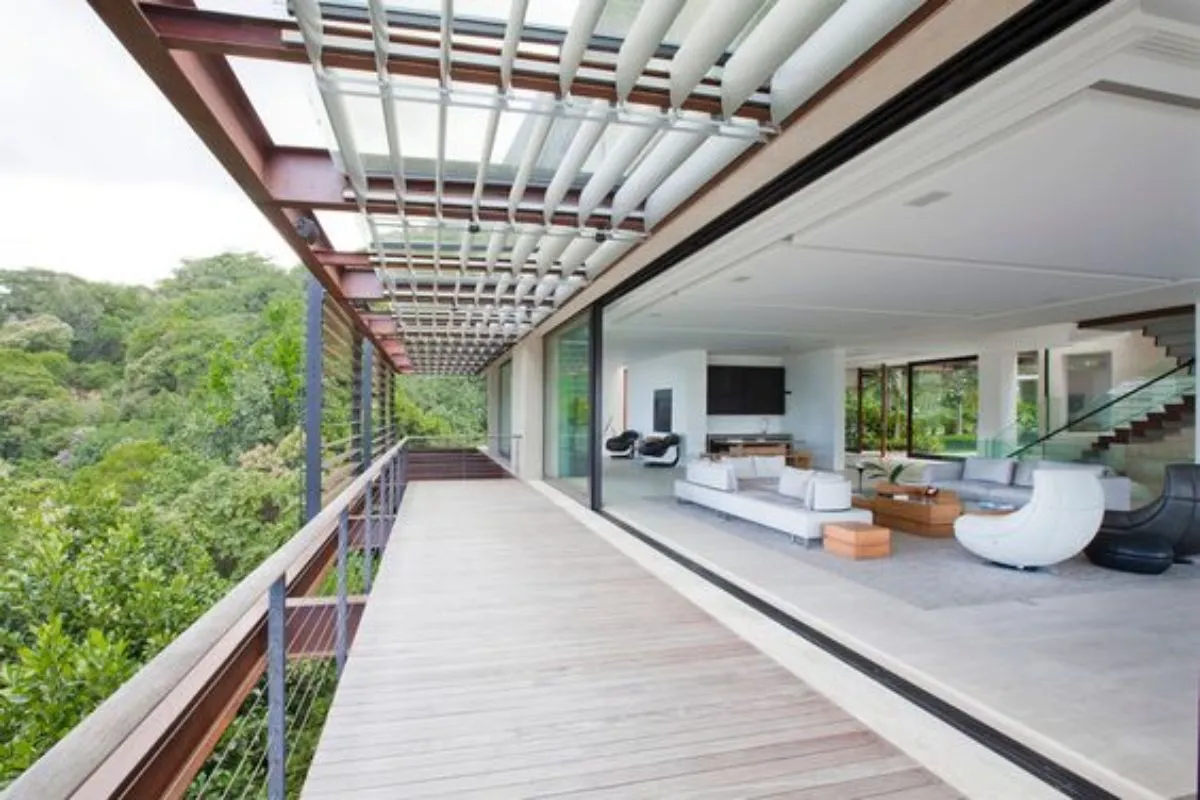
Passive Cooling Architecture: A Sustainable Solution for Homeowners
Passive cooling architecture refers to design strategies that naturally regulate indoor temperatures without relying on mechanical cooling systems. This eco-friendly approach is becoming increasingly essential for homeowners looking to reduce energy consumption, enhance comfort, and embrace sustainable living practices.
What is Passive Cooling?
Passive cooling is a concept that utilizes natural processes to maintain comfortable indoor environments. By employing architectural design elements, materials, and landscaping, homeowners can optimize airflow and minimize heat gain. Common passive cooling strategies include:
- Building Orientation: Positioning the structure to maximize natural ventilation and minimize sun exposure.
- Thermal Mass: Using materials that absorb heat during the day and release it at night.
- Shading Techniques: Incorporating overhangs, awnings, and landscaping to block direct sunlight.
- Natural Ventilation: Creating airflow paths through windows, doors, and vents to cool spaces.
Why Choose Passive Cooling?
The choice of passive cooling over traditional air conditioning systems provides numerous benefits that align with sustainable living:
1. Energy Efficiency
Adopting passive cooling techniques can significantly lower energy bills. Studies indicate that homes designed with passive cooling can decrease energy consumption by up to 50%. This reduction not only benefits homeowners financially but also reduces the strain on the energy grid.
2. Enhanced Indoor Comfort
Properly designed passive cooling systems stabilize indoor temperatures, resulting in improved comfort levels. This is especially crucial in regions with hot climates, where prolonged exposure to heat can lead to health risks.
3. Positive Environmental Impact
By minimizing energy consumption, passive cooling directly contributes to a smaller carbon footprint. Homeowners who implement these strategies support sustainable living and help combat climate change.
4. Low Maintenance Requirements
Unlike mechanical cooling systems that require regular maintenance, many passive cooling techniques involve minimal upkeep. This leads to reduced long-term costs and less hassle for homeowners.
5. Increased Property Value
Homes that incorporate energy-efficient features, including passive cooling, are increasingly desirable. Implementing these strategies can enhance property value and appeal to eco-conscious buyers.
Key Passive Cooling Techniques
Here are effective passive cooling strategies that homeowners can implement:
1. Strategic Orientation
- South-Facing Windows: Maximize sunlight during winter months and minimize heat gain in summer.
- Cross Ventilation: Design openings on opposite sides of the house to facilitate natural airflow.
2. Thermal Mass Utilization
- Material Selection: Incorporate materials like concrete, brick, or stone that absorb heat during the day and release it at night.
- Flooring Choices: Use tile or polished concrete floors to enhance thermal mass properties.
3. Effective Shading
- Overhangs and Awnings: Install roof overhangs that block high summer sun while allowing lower winter sun to enter living spaces.
- Landscaping: Plant deciduous trees near windows to provide shade in summer and sunlight in winter.
4. Natural Ventilation Strategies
- Operable Windows: Install windows that can be opened to create cross-ventilation. Consider placing them in strategic locations to maximize airflow.
- Ventilation Towers: Design ventilation towers or chimneys that draw hot air upward, enhancing natural airflow throughout the home.
5. Cool Roofs and Green Roofs
- Reflective Materials: Use roofing materials that reflect sunlight, thus reducing heat absorption and keeping interiors cooler.
- Vegetation on Roofs: Planting vegetation on rooftops provides additional insulation and helps mitigate heat buildup.
Integrating Passive Cooling with Other Sustainable Practices
To maximize the benefits of passive cooling architecture, homeowners can integrate these strategies with other sustainable practices, such as:
1. Renewable Energy Sources
Utilizing solar panels in conjunction with passive cooling can significantly reduce energy costs. Solar energy can power household appliances and systems, further minimizing reliance on the grid.
2. Efficient Insulation
Proper insulation complements passive cooling strategies by preventing heat transfer. This means that homes stay cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter, enhancing overall energy efficiency.
3. Smart Home Technology
Incorporating smart home devices can optimize the effectiveness of passive cooling techniques. For instance, programmable thermostats can adjust the temperature based on weather conditions, enhancing comfort and energy efficiency.
Conclusion
Passive cooling architecture offers homeowners a sustainable and efficient way to enhance indoor comfort while reducing energy consumption and environmental impact. By implementing strategies such as strategic orientation, thermal mass utilization, effective shading, natural ventilation, and cool roofs, homeowners can significantly improve their living conditions.
Embracing passive cooling not only supports a sustainable lifestyle but also increases property value, making it a wise investment for the future. As the demand for eco-friendly homes rises, understanding and applying passive cooling techniques is more important than ever.