The Benefits of Geothermal Heating and Cooling Systems
As concerns about climate change and energy consumption continue to grow, the search for sustainable and efficient energy solutions has become more crucial than ever. Among the many innovative technologies available, geothermal heating and cooling systems stand out as a highly effective and eco-friendly option. Harnessing the Earth’s natural heat, these systems provide a reliable and renewable source of energy for both residential and commercial buildings. In this article, we will explore the myriad benefits of geothermal heating and cooling systems, examining their environmental impact, cost-effectiveness, and overall efficiency.
Understanding Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is derived from the natural heat stored within the Earth’s crust. This heat originates from the radioactive decay of minerals and the original formation of the planet, providing a constant and inexhaustible source of energy. Unlike traditional fossil fuels, geothermal energy is not subject to the fluctuations and limitations of external factors, making it a stable and sustainable option.
How Geothermal Systems Work
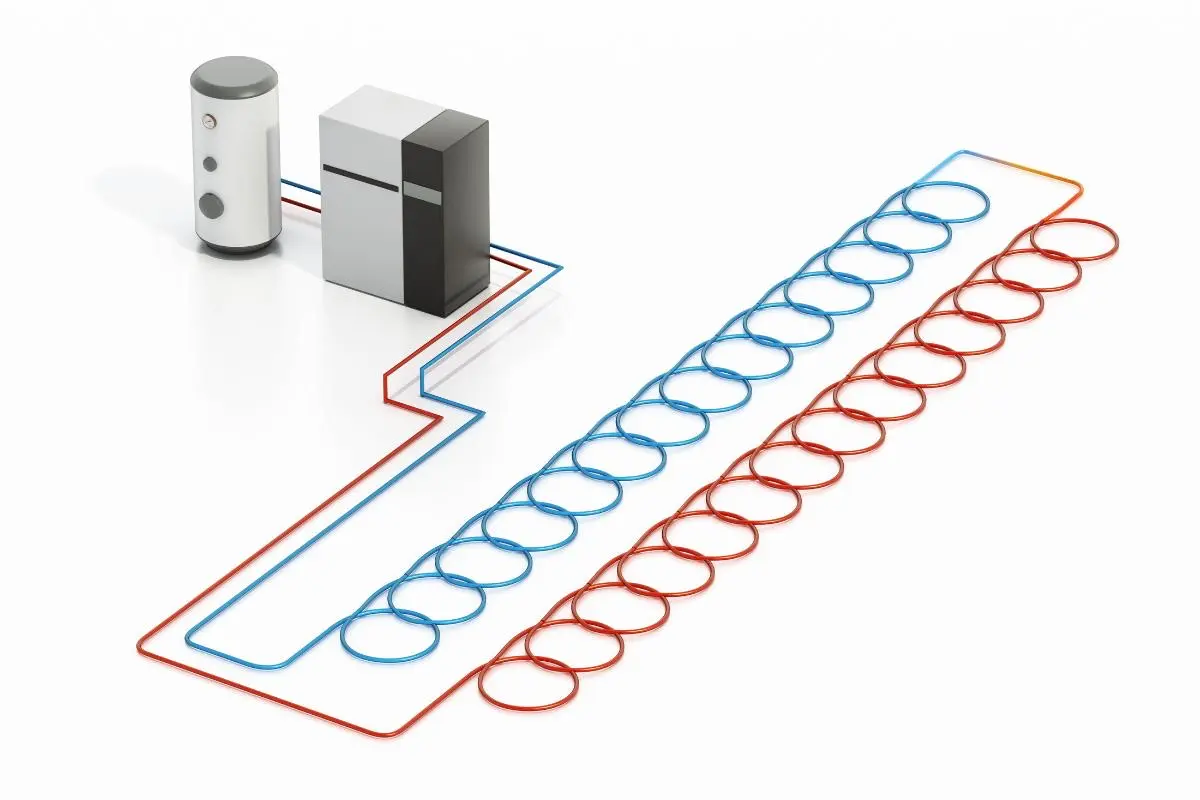
Geothermal heating and cooling systems operate by utilizing a series of pipes, known as a loop, buried underground. These loops circulate a fluid that absorbs heat from the Earth during the winter and releases heat back into the ground during the summer. A heat pump then transfers this energy to heat or cool the building, providing a comfortable indoor climate year-round. This process is highly efficient, with geothermal systems capable of achieving efficiencies of up to 400%, meaning they produce four units of energy for every unit of electricity consumed.
Environmental Benefits
One of the most significant advantages of geothermal heating and cooling systems is their positive impact on the environment. Traditional heating and cooling methods often rely on fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. In contrast, geothermal systems use the Earth’s natural heat, significantly reducing the carbon footprint of buildings.
Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Geothermal systems produce minimal greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional heating and cooling systems. By utilizing a renewable energy source, they help reduce the reliance on fossil fuels, leading to a significant decrease in carbon dioxide and other harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere. This reduction is crucial in mitigating the effects of climate change and promoting cleaner air quality.
Conservation of Natural Resources
Another environmental benefit of geothermal systems is their ability to conserve natural resources. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and depleting, geothermal energy is abundant and inexhaustible. By tapping into this sustainable resource, we can reduce our dependence on non-renewable energy sources, ensuring a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Economic Advantages
In addition to their environmental benefits, geothermal heating and cooling systems also offer significant economic advantages. Although the initial installation costs can be higher than traditional systems, the long-term savings and financial incentives make them a wise investment.
Lower Operating Costs
Geothermal systems are known for their exceptional efficiency, resulting in lower operating costs compared to conventional heating and cooling methods. By utilizing the Earth’s stable temperatures, these systems require less energy to maintain a comfortable indoor climate. Homeowners and businesses can experience significant savings on their energy bills, often reducing costs by up to 70%.
Financial Incentives and Rebates
To encourage the adoption of renewable energy technologies, many governments and utility companies offer financial incentives and rebates for installing geothermal systems. These incentives can help offset the initial installation costs, making geothermal systems more accessible and affordable. Additionally, some regions offer tax credits and grants, further enhancing the economic viability of these systems.
Enhanced Comfort and Reliability
Beyond the environmental and economic benefits, geothermal heating and cooling systems also provide enhanced comfort and reliability. Their unique design and operation ensure consistent indoor temperatures and a high level of reliability.
Consistent Indoor Temperatures
Geothermal systems maintain consistent indoor temperatures by utilizing the Earth’s stable heat. Unlike traditional systems that can experience fluctuations and uneven heating or cooling, geothermal systems provide a steady and comfortable climate throughout the year. This consistency enhances indoor comfort, ensuring a pleasant living or working environment.
Longevity and Durability
Geothermal systems are known for their longevity and durability. The underground loops have a lifespan of up to 50 years, while the heat pump can last up to 25 years with proper maintenance. This durability reduces the need for frequent replacements and repairs, providing long-term reliability and peace of mind for homeowners and businesses.
Installation Process of Geothermal Systems
The installation of geothermal heating and cooling systems is a detailed process that requires careful planning and execution. Although it involves a higher upfront investment, the long-term benefits far outweigh the initial costs. Here, we break down the essential steps involved in installing a geothermal system.
Site Evaluation and System Design
Before installation begins, a thorough site evaluation is necessary to determine the suitability of geothermal energy for the property. This evaluation includes soil analysis, groundwater availability, and the size and layout of the land. Based on this data, engineers design a customized geothermal system that meets the specific heating and cooling needs of the building.
Loop System Installation
The next step involves the installation of the loop system, which is the core component of a geothermal setup. There are three main types of loop systems: horizontal, vertical, and pond/lake.
- Horizontal loops: These are installed in trenches dug about 4 to 6 feet deep. They are suitable for properties with ample land space.
- Vertical loops: These are installed in boreholes drilled hundreds of feet into the ground, ideal for properties with limited land space or for larger buildings.
- Pond/lake loops: These are laid at the bottom of a nearby water body, utilizing the consistent temperatures of the water.
Once the loop type is selected based on the site evaluation, the appropriate loops are installed and connected to the geothermal heat pump inside the building.
Heat Pump Installation
The geothermal heat pump, typically installed indoors, is the system’s heart. It extracts heat from the fluid circulating in the loop system and transfers it to the building during the winter. In summer, the process reverses, and the heat pump transfers heat from the building back into the ground. This installation involves connecting the heat pump to the loop system and integrating it with the building’s existing HVAC system.
System Testing and Commissioning
After installation, the system undergoes rigorous testing to ensure all components function correctly. Technicians will check for leaks, ensure proper fluid circulation, and verify the heat pump’s operation. Once confirmed, the system is commissioned and ready for use, providing efficient heating and cooling for the property.
Case Studies of Successful Implementations
To understand the real-world impact of geothermal systems, let’s explore some successful case studies where these systems have revolutionized energy consumption and sustainability.
Residential Case Study: The Smith Family Home
The Smith family, residing in a suburban area, decided to switch to a geothermal heating and cooling system to reduce their carbon footprint and energy bills. After a detailed site evaluation, a horizontal loop system was installed on their 2-acre property.
Results:
- Energy Savings: The Smiths saw a 60% reduction in their energy bills within the first year.
- Comfort: The family reported more consistent indoor temperatures and improved overall comfort.
- Environmental Impact: The switch to geothermal energy reduced the household’s carbon emissions by approximately 5 tons annually.
Commercial Case Study: Green Office Complex
A large office complex aiming for LEED certification chose geothermal energy as part of its sustainability strategy. Due to space constraints, a vertical loop system was installed beneath the building’s parking lot.
Results:
- Cost Savings: The office complex reduced its heating and cooling costs by 50%, recouping the installation costs within 7 years.
- Sustainability: The geothermal system contributed significantly to the building achieving LEED Gold certification.
- Employee Comfort: Employees reported a more stable and comfortable working environment, which also boosted productivity.
Maintenance and Optimization Tips
While geothermal systems are known for their durability, regular maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Here are some key tips for maintaining and optimizing your geothermal heating and cooling system:
Regular Inspections
Conduct regular inspections of the entire system, including the loop field and heat pump. Look for any signs of wear, leaks, or damage, and address issues promptly to prevent larger problems.
Fluid Level Checks
Monitor the fluid levels in the loop system to ensure there is adequate circulation. Low fluid levels can reduce the system’s efficiency and may indicate leaks.
Heat Pump Maintenance
The heat pump requires routine maintenance, similar to traditional HVAC systems. This includes cleaning or replacing filters, checking refrigerant levels, and ensuring the system is free of debris.
Professional Servicing
Schedule annual professional servicing to keep your geothermal system in top condition. Certified technicians can perform comprehensive checks, calibrate the system, and make any necessary adjustments to enhance efficiency.
Conclusion
Geothermal heating and cooling systems offer an array of benefits, from environmental sustainability and significant cost savings to enhanced indoor comfort and reliability. By tapping into the Earth’s natural heat, these systems provide a clean, renewable energy source that can dramatically reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate the impact of climate change.